7T MRI and layer-specific imaging
2019
Recent developments of ultra-high-field fMRI provided an opportunity to investigate neural activities across cortical layers and columns in the human brain.
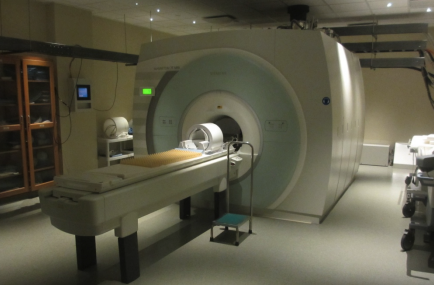
7T Siemens MRI machine at NIH
Actively shielded, body gradient, sub-mm anatomical (T1,T2) and funcitonal images (EPI)
Actively shielded, body gradient, sub-mm anatomical (T1,T2) and funcitonal images (EPI)
A higher magnetic field usually means higher imaging resolution. Previously, it was almost impossible to measure layer-specific neuronal activities in the living human brain. With the development of 7T MRI and an advanced fMRI imaging sequence (VASO), we can now push the fMRI resolution to be up to 0.8 mm. The thickness of the human visual cortex is usually around 2.5 ~ 3 mm, which means that we can obtain around 3 voxels across cortical depth (0.8 mm * 3 voxels = 2.4 mm)

Layers provide information about directionality. Investigating relative contributions of each layer give insights into how feedforward and feedback information is processed.
Defining V1 Layers

- Manual parcellation of gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Interpolated to 9 layers using equal Euclidean distances
V1 activation profile (Stimulus - Blank)

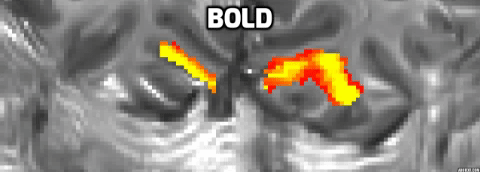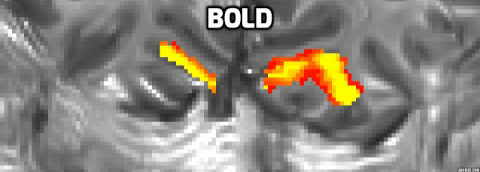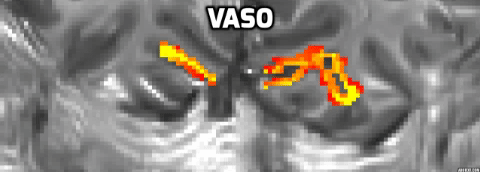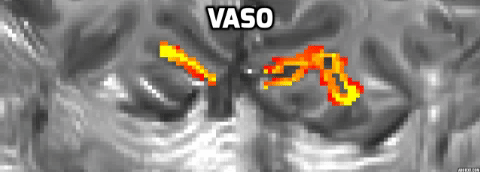
Distinct layer profiles for two differnt imaging seqeunces: BOLD and VASO.
BOLD sequence suffers from a blood drainage problem. BOLD showed a higher signal towards the upper layer, while VASO peaked towards the middle layer.
Decoding Orientation across layers
Support Vector Machine, SVM
Top 75 % voxel-selection
Chance level: 16.6%
![]()

-
BOLD & VASO higher than chance decodability across layers
- BOLD showed no specific pattern across layers, although a strong feed-forward signal towards the middle and deep layer was expected
- Overall, VASO showed higher decodability than BOLD, although BOLD had higher signal change compared to VASO in the time series data.
- VASO showed layer-specific decoding that corresponds to known feed-forward signals having the highest decodability towards the middle layer, while BOLD did not.